Radiological imaging is a cornerstone of modern medicine, allowing healthcare professionals to peer inside the human body non-invasively. In this blog post, we will explore the various types of radiological imaging modalities, their unique principles, and when they are most commonly used in the medical field.
Section 1: X-Rays
X-ray imaging is one of the oldest and most widely recognized forms of radiological imaging.
- Principle: X-rays are high-energy electromagnetic waves that pass through the body, creating a shadowy image of bones and dense tissues on a detector.
- Applications: X-rays are commonly used for diagnosing fractures, dental issues, chest conditions, and locating foreign objects.
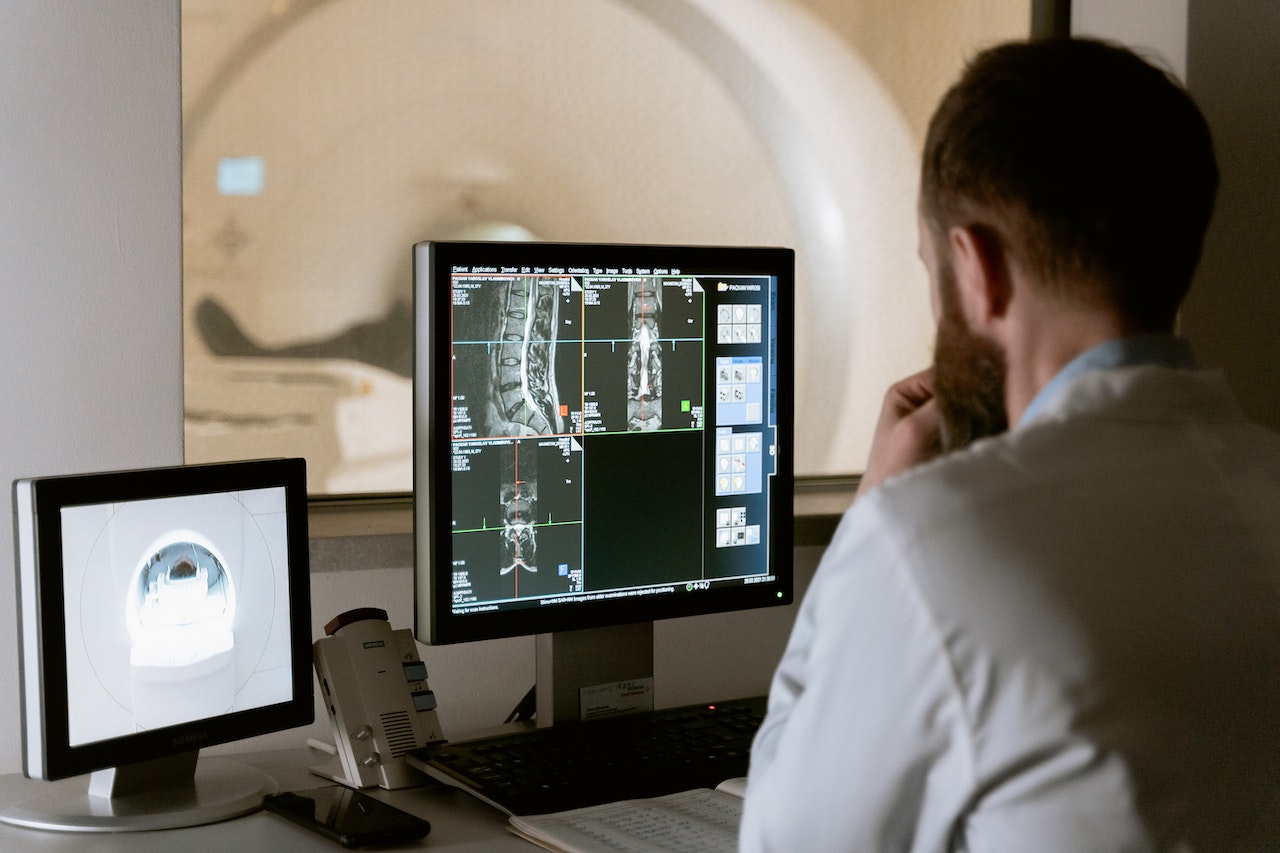
Section 2: Computed Tomography (CT) Scans
CT scans provide detailed cross-sectional images of the body.
- Principle: CT scans use a rotating X-ray machine to capture multiple images from different angles, which are then reconstructed into detailed 3D images.
- Applications: CT scans are valuable for visualizing soft tissues, detecting tumors, and assessing internal injuries, such as those from trauma.
Section 3: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI uses strong magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of soft tissues.
- Principle: MRI relies on the behavior of hydrogen atoms in the body’s tissues when exposed to a magnetic field and radio waves.
- Applications: MRI is ideal for assessing the brain, spinal cord, muscles, joints, and abdominal organs. It is often used for neurological, musculoskeletal, and abdominal evaluations.
Section 4: Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to produce real-time images.
- Principle: Ultrasound machines emit sound waves into the body, and the echoes produced by bouncing off tissues create images.
- Applications: Ultrasound is widely used for monitoring pregnancy, evaluating the heart, visualizing blood flow, and assessing organs like the liver, kidneys, and thyroid.
Section 5: Nuclear Medicine Imaging
Nuclear medicine involves the use of radioactive substances to create images of the body’s functions.
- Principle: Patients are given a radioactive tracer, which accumulates in specific organs or tissues. A gamma camera captures the emissions from the tracer.
- Applications: Nuclear medicine is used for studying organ function, assessing bone health, and detecting certain types of cancer, such as thyroid and prostate cancer.
Section 6: Choosing the Right Modality
Selecting the appropriate imaging modality depends on the clinical question and the area of the body being examined.
- Considerations: Factors to consider include the type of condition being investigated, the need for real-time imaging, and the patient’s health status.
Conclusion:
Each radiological imaging modality offers unique insights into the human body, making it possible for healthcare professionals to diagnose and treat a wide range of medical conditions effectively. At [Your Radiology Service], we offer a comprehensive suite of imaging modalities to ensure that our patients receive the most accurate and tailored diagnostic information for their healthcare needs.
Call to Action:
If you have questions about which radiological imaging modality is right for you or if you need to schedule an imaging appointment, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us. Our team of experts is here to guide you on your healthcare journey.